Types of Unconformities 40
Types of Unconformities 40
Types of Unconformities 40
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The Rock Record<br />
TEACHING TRANSPARENCY<br />
<strong>Types</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Unconformities</strong> <strong>40</strong><br />
<strong>Types</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Unconformities</strong><br />
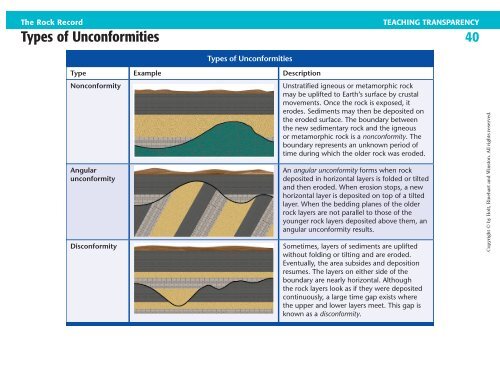
Type Example Description<br />
Nonconformity<br />
Angular<br />
unconformity<br />
Disconformity<br />
Unstratified igneous or metamorphic rock<br />
may be uplifted to Earth’s surface by crustal<br />
movements. Once the rock is exposed, it<br />
erodes. Sediments may then be deposited on<br />
the eroded surface. The boundary between<br />
the new sedimentary rock and the igneous<br />
or metamorphic rock is a nonconformity. The<br />
boundary represents an unknown period <strong>of</strong><br />
time during which the older rock was eroded.<br />
An angular unconformity forms when rock<br />
deposited in horizontal layers is folded or tilted<br />
and then eroded. When erosion stops, a new<br />
horizontal layer is deposited on top <strong>of</strong> a tilted<br />
layer. When the bedding planes <strong>of</strong> the older<br />
rock layers are not parallel to those <strong>of</strong> the<br />
younger rock layers deposited above them, an<br />
angular unconformity results.<br />
Sometimes, layers <strong>of</strong> sediments are uplifted<br />
without folding or tilting and are eroded.<br />
Eventually, the area subsides and deposition<br />
resumes. The layers on either side <strong>of</strong> the<br />
boundary are nearly horizontal. Although<br />
the rock layers look as if they were deposited<br />
continuously, a large time gap exists where<br />
the upper and lower layers meet. This gap is<br />
known as a disconformity.<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Name Class Date<br />
Transparency Worksheet<br />
<strong>Types</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Unconformities</strong><br />
1. How do noncomformities differ from angular conformities and<br />
disconformities?<br />
2. Why do unconformities represent a break in the geologic record?<br />
3. In a nonconformity, what types <strong>of</strong> rock underlie the sedimentary rock?<br />
4. Which type <strong>of</strong> unconformity do you think is the most difficult to detect?<br />
Explain your answer.<br />
5. The geologic processes <strong>of</strong> uplifting and folding would most likely precede<br />
which type <strong>of</strong> unconformity?<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.<br />
Holt Earth Science<br />
The Rock Record
ANSWER KEY<br />
2. the turbine<br />
3. a generator<br />
4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: The<br />
turbine spins rapidly to generate electricity.<br />
Fish would have to pass through<br />
it to get past the dam.<br />
5. Answers may vary. Sample answer:<br />
Yes, but a smaller amount <strong>of</strong> electricity<br />
would be generated.<br />
38 Wind Power in the United States<br />
1. WY and AK<br />
2. CA and WA<br />
3. TX<br />
4. the Rocky Mountains<br />
5. TX<br />
6. The comparison means that these<br />
states could be a major source <strong>of</strong> wind<br />
energy, much as Saudi Arabia is a<br />
major source <strong>of</strong> oil.<br />
39 Law <strong>of</strong> Superposition<br />
1. sedimentary rock<br />
2. that the rock layer is underformed<br />
3. Sedimentary layers will always be<br />
deposited on top <strong>of</strong> metamorphic rock<br />
or large igneous rock masses. Igneous<br />
rock from volcanic eruptions can be<br />
deposited as part <strong>of</strong> the rock sequence.<br />
4. Layer B is older than layer C, because<br />
the law <strong>of</strong> superposition dictates that<br />
an underformed rock layer is older<br />
than the layers above it.<br />
<strong>40</strong> <strong>Types</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Unconformities</strong><br />
1. Nonconformities involve layers <strong>of</strong><br />
sedimentary rock that form on top <strong>of</strong><br />
unstratified rock. Angular unconformities<br />
and disconformities both involve<br />
sedimentary rock layers that form on<br />
top <strong>of</strong> stratified rock.<br />
2. <strong>Unconformities</strong> indicate that a rock<br />
layer was exposed to erosion for a<br />
period <strong>of</strong> time before the overlying sedimentary<br />
layers were deposited. This<br />
erosional period creates a break in the<br />
geologic record.<br />
3. metamorphic or igneous rock<br />
4. a disconformity, because all <strong>of</strong> the rock<br />
layers are stratified and horizontal<br />
5. an angular unconformity<br />
41 Crosscutting Relationships<br />
1. the fault, because the law <strong>of</strong> crosscutting<br />
relationships states that the fault is<br />
younger than the rock it cuts<br />
2. Faulting must have occurred most<br />
recently because it cuts through all the<br />
layers <strong>of</strong> rock and the intrusion.<br />
3. The igneous intrusion is younger<br />
because it cuts through layer C.<br />
4. No. Either could have formed after<br />
layer C was deposited but before faulting<br />
occurred.<br />
42 Radioactive Decay and Half-Life<br />
1. In beta decay, a neutron gives <strong>of</strong>f a<br />
beta particle. In alpha decay, an alpha<br />
particle consisting <strong>of</strong> two protons and<br />
two neutrons is emitted.<br />
2. The mass <strong>of</strong> the atom decreases<br />
because the atom loses two protons<br />
and two neutrons that make up the<br />
alpha particle.<br />
3. 4<br />
4. one-half<br />
5. after one half-life<br />
43 Geologic Map <strong>of</strong> Bedrock in Ohio<br />
1. the Permian, Pennsylavanian,<br />
Mississippian, devonian, Silurian, and<br />
Ordovician<br />
2. The youngest bedrock is in the southeastern<br />
part <strong>of</strong> the state; the oldest bedrock<br />
is in the western part <strong>of</strong> the state.<br />
3. In traveling east to west, the bedrock<br />
would generally become older.<br />
4. The bedrock layers are tilted upwards.<br />
The more horizontal surface <strong>of</strong> earth<br />
cuts across the angled layers and thus<br />
exposes them. If the layers were horizontal,<br />
only the top, or youngest layer<br />
wuld be exposed.<br />
5. because Mississippian rock was formed<br />
in the Mississippian Period just after the<br />
rock formed in the Devonian Period<br />
6. To find early reptile fossils you’d look<br />
in Pennsylvanian rock, represented by<br />
the color blue, which occurs in a large<br />
stripe extending to the southwest from<br />
eastern Ohio.<br />
44 The Geologic Time Scale<br />
1. More recent rocks have been altered or<br />
eroded less than older rocks have and<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.<br />
Holt Earth Science 12 Answer Key