Situational motivation is the most common learning motivation of students. The interference of cultural environment will directly affect students’ learning enthusiasm and achievement. Andrews (2011) analyzed the influence of situational motivation on intrinsic interest, challenge, control of learning situation and social interaction. Therefore, we can see that learning motivation is the ultimate goal to be achieved by students, and constructivism provides theoretical support for situational learning. Here’s the relationship:
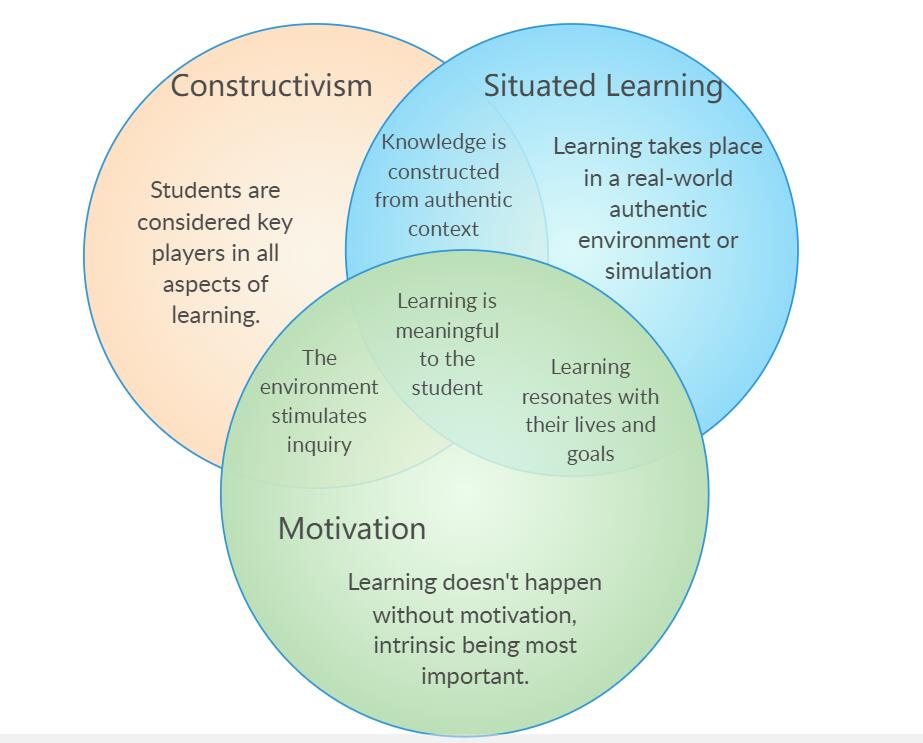
In the classroom of constructivism, students are the most important learning role, so whether students’ thinking is correct or not is related to their understanding of concepts and cultural background, and the understanding of these correct and wrong concepts is a very important link in students’ learning process. Therefore, the constructivism view holds that knowledge is fluid and constantly changing, and only when students successfully expand and explore this view instead of passive learning can they achieve learning achievement. But in this process, teachers should pay attention to the importance of building students’ values and accept and encourage students’ critical thinking instead of giving absolute and fixed answers. Teachers also seek solutions through various channels and resources to encourage students to think deeply. At the same time, the key way to mobilize students’ motivation is to stimulate their interest. It is necessary for teachers to seek the teaching support from the cultural environment according to the theme setting.
Culture provides students with cognitive tools for their development. Language, cultural history, social background and electronic acquisition forms in the society can all be transmitted through teaching. “Knowledge is to be taken seriously only if it claims to represent a world of “things-in-themselves” in a more or less veridical fashion”(von Glasersfeld, 1990). This may be why student motivation is associated with realistic knowledge. Therefore, environment design can stimulate students’ thinking, help students develop effective thinking skills and attitudes, and contribute to effective problem solving and critical thinking. The picture below is a tip about how teachers use language to encourage students.

References:
Andrews, E. (2011, May 16). What is motivation? Retrieved December 8, 2014, from http://www.examiner.com/article/what-is-motivation
Von Glasersfeld, E. (1991). An exposition of constructivism: Why some like it radical. In Facets of systems science (pp. 229-238). Springer, Boston, MA.