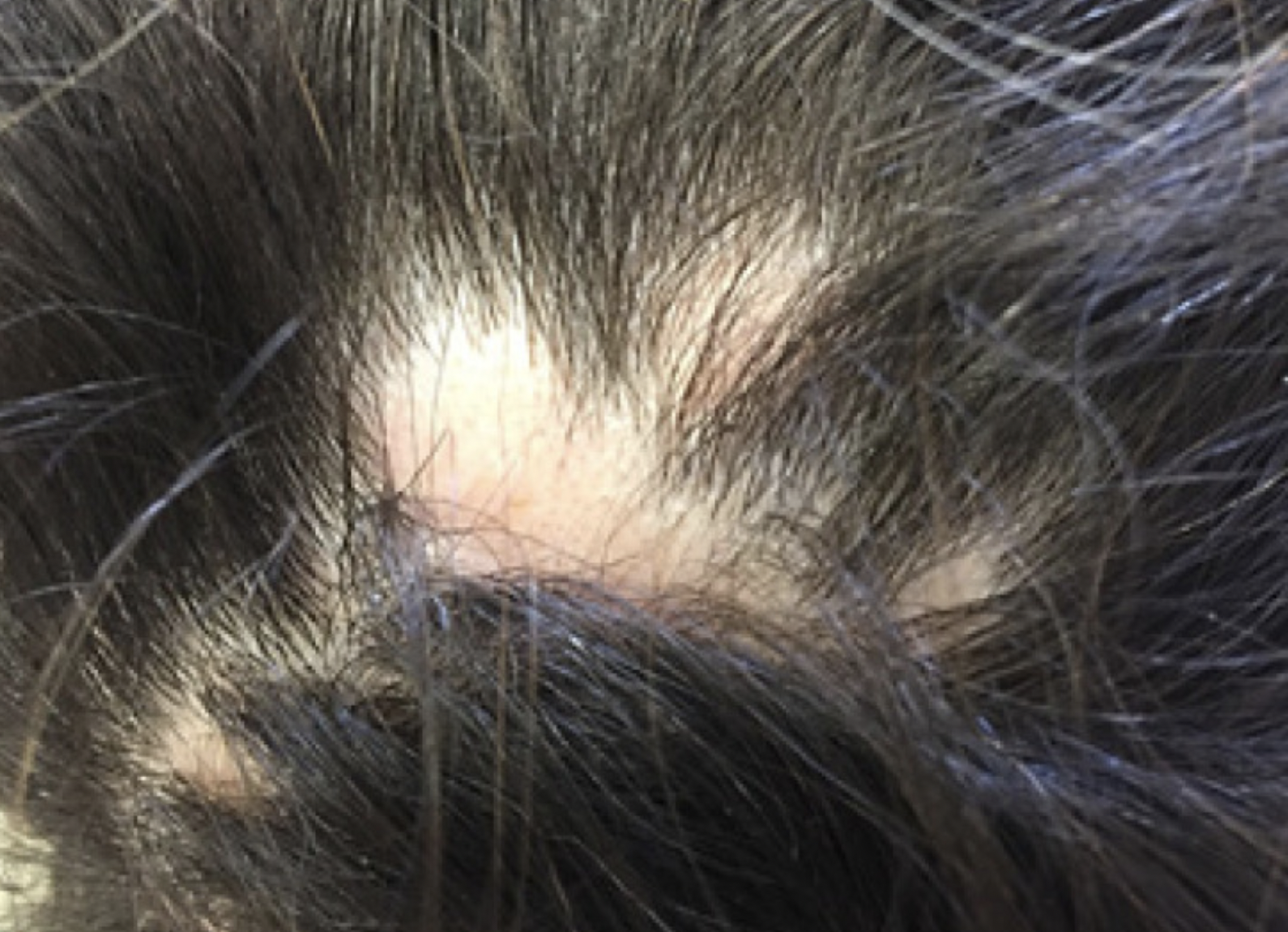
Hair Loss: What's causing my hair loss?
What’s causing my patch of hair loss?
I’ve selected this question below for this week’s question of the week. It allows us to review some concepts regarding clinical and trichoscopic examination of acute hair loss.
Question
Hi Dr. Donovan.
I’m a 31 year old female. While giving birth I almost died, went in to septic shock and lost a massive amount of blood. 2.5 months later I lost a lot of hair, I had thinning all over but more obvious around my ears, sides of my head and on the nape of my neck. My dermatologist (and biopsy) said it was TE and gave me steroid shots and my hair is growing back normally with no thinning.
I developed seborrheic dermatitis, my head is a little itchy and I’m on ketoconazole shampoo. 5 months after birth, I had to have major surgery on my kidney, the surgery itself lasted 8 hours. On the 2nd or 3rd day at the hospital I noticed a painful bump on my parietal lobe. On the 19th day after surgery, I washed my hair and then noticed the hair loss on the same area as the swelling. Ive attached photos of the first time noticing it.
My dermatologist injected it with steroids and it isn’t growing back. It’s been 3.5 months since it fell out. There are tiny hairs in the area so my dermatologist is sure it isn’t scarred.
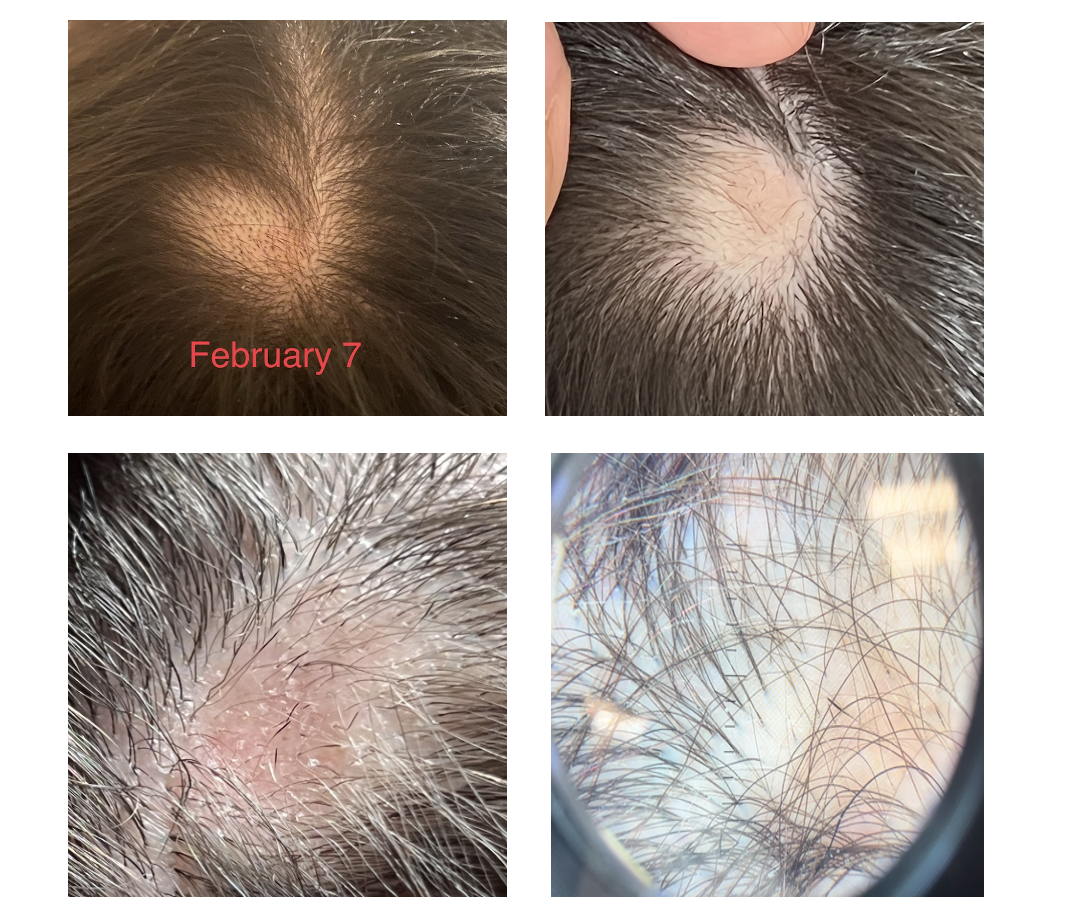
But there are also exclamation looking hairs so we are not sure. The area is reddish. I have no hair loss anywhere else. It hasn’t gotten bigger and I don’t have any patches elsewhere. The picture labeled February 7 is the day I noticed it.
Answer
Thanks for submitting this question. I hope that you are feeling well. At first overview, it certainly would appear that the diagnosis is alopecia areata with some overlapping findings of seborrheic dermatitis. In addition, it appears that you first had a telogen effluvium (of alopecia areata again) that settled after delivery. I still favour alopecia areata as the diagnosis in the current photos but there are a few things in your story and some of your images that cause me to pause and ask “is it possible there is anything else going on here?”
The reason I’ve chosen this question is that it allows us to review some of these features today.
There are several scalp conditions that can cause localized hair loss in this manner with possible ‘exclamation mark like hairs”. The top 4 include:
alopecia areata ** most likely **
dissecting cellulitis
pseudocysts (alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp
infections (syphilitic alopecia)
Other diagnoses to consider here but do not have good evidence include:
tinea capitis
pressure alopecia
infiltrative conditions.
trichotillomania
Let’s take a look first at some of the images supplied in this question and then we’ll go into these possibilities a little further and come to some conclusions.
Submitted Image 1
This image shows patchy hair loss. There are broken hairs. Inflammation is mild. The top diagnosis at this magnification would be alopecia areata. The differential diagnosis from this image might include trichotillomania, tinea capitis, and pressure induced alopecia. Alopecia areata would be the top diagnosis. Exclamation mark hairs are not clearly seen in this image but are seen in other images. There is no evidence for a scarring alopecia. Density may be reduced in the more anterior portion of the scalp (top of the photo) suggesting ongoing TE or another hair loss diagnosis happening in this area.
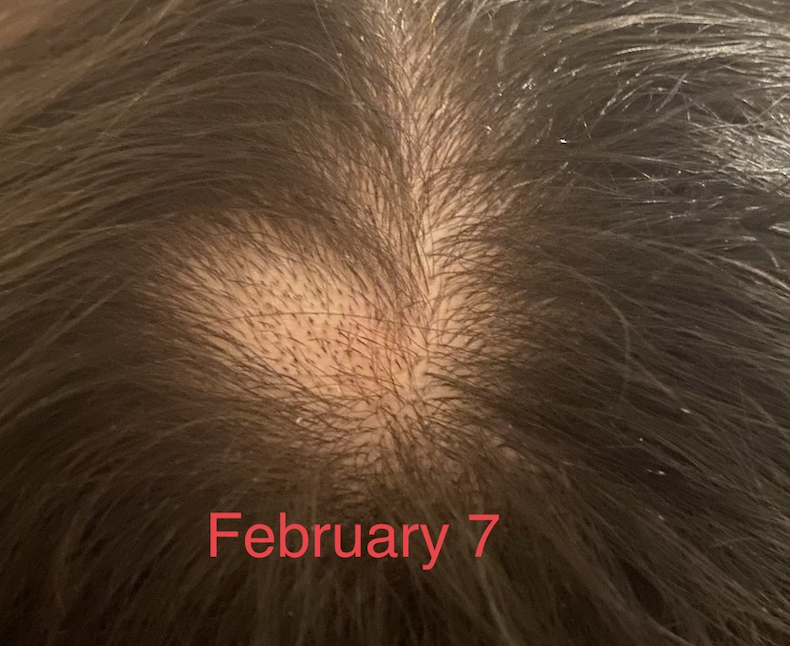
Submitted Image 2
This image shows a well cicumscribed area with minimal inflammation. There are vellus hairs and broken hairs. Some hairs have hair shaft changes suggestive of a pseudo-monilthrix like change (Pohl Pinkus constrictions). Exclamation mark hairs are not clearly seen in this image but are seen in other images. There is no good evidence for a scarring alopecia. Alopecia areata remains a favoured diagnosis.
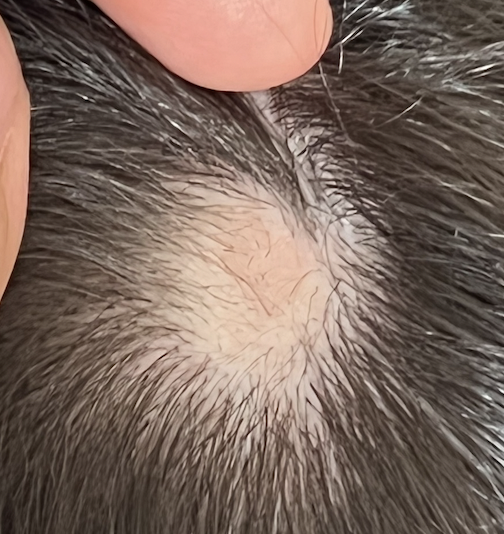
Submitted Image 3
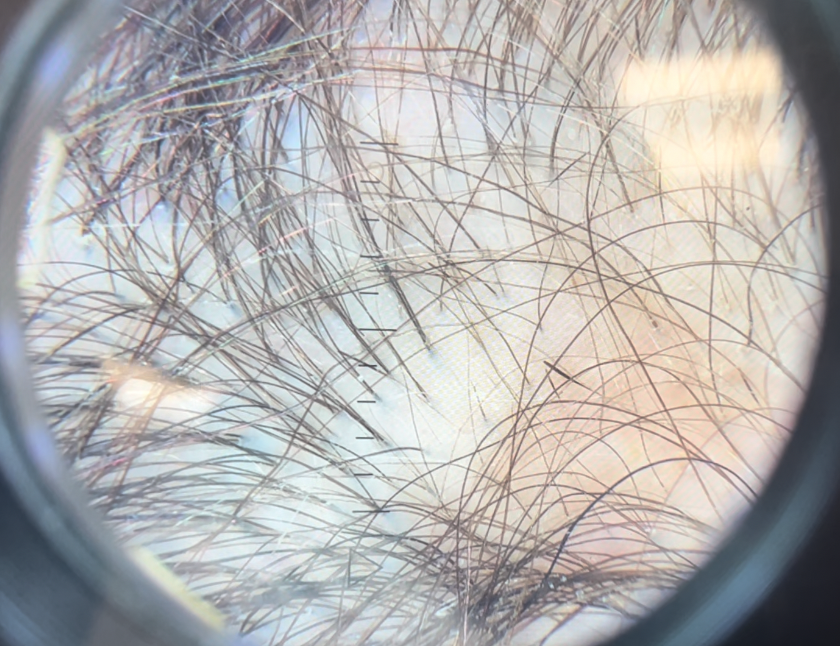
Numerous exclamation mark hairs are seen in this image. Elbow hairs are seen. Yellow dots are seen. There is an inflammatory type change with whitish scale. There is a mild pigmentation alteration which is somewhat non specific. The exclamation mark hairs make other diagnoses quite unlikely as exclamation mark hairs of this kind do not occur in pressure alopecia nor in inflammatory connective issues issues. The appearance of the scalp in this image differs quite a bit from the appearance seen in other images.
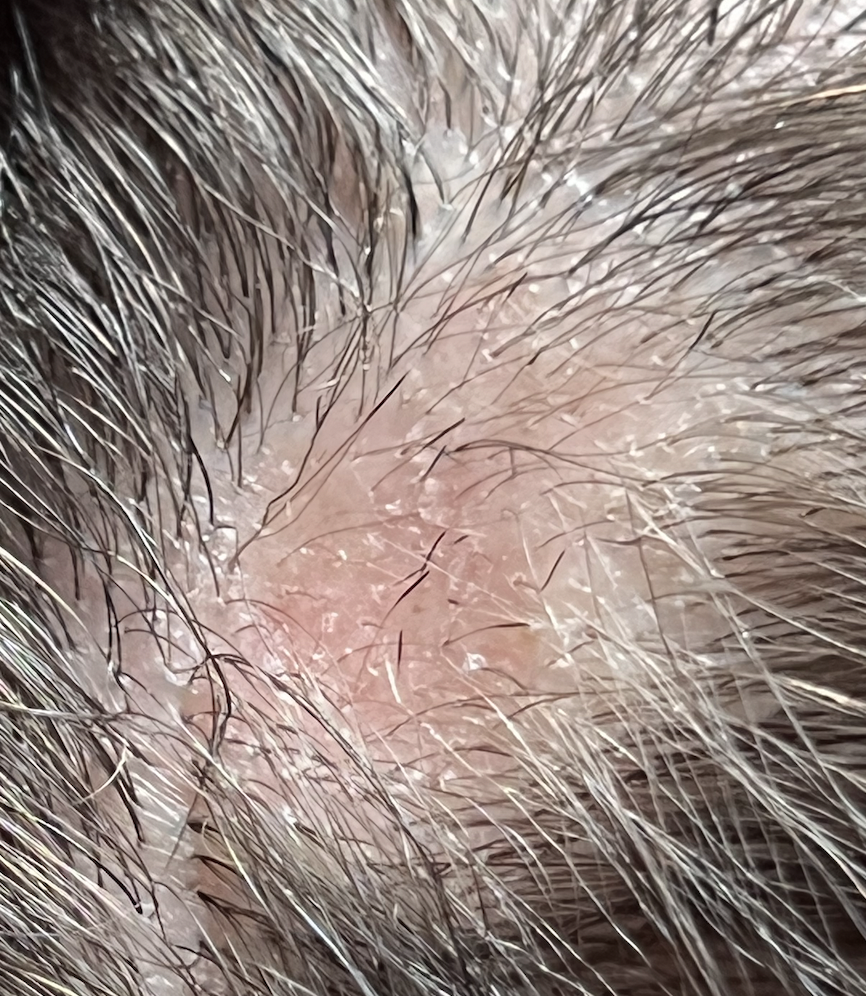
Submitted Image 4
This image shows several exclamation mark hairs with regrowing vellus hairs. There is mild yellow scale which may be in keeping with seborrheic dermatitis (of psoriasis) or an artefact of the photo itself. There is no evidence for a scarring alopecia.
Further Discussion
Thanks again for submitting this case. I favour alopecia areata but of course it’s nice to have more information and see the entire scalp eyebrows eyelashes, and nails. The most accurate way to diagnosis hair loss is to collect all the information about the patient and then examine all the scalp.
The features that support alopecia areata are the exclamation mark hairs, vellus hairs, regrowing hairs and localized nature of the hair loss.
What other conditions cause exclamation mark hairs?
As we think about this question, it’s helpful to think about all that conditions that cause exclamation mark hairs. After all, one of the key features in the submitted images are the exclamation mark hairs.
Exclamation mark hairs are seen in alopecia areata, trichotillomania, thallium poisoning, dissecting cellulitis. Syphilitic alopecia has been rarely described to have a type of tapered hair closely resembling a true exclamation mark hair. This is very rare.
Trichotillomania
There does not appear to be good evidence here for trichotillomania. The story does not fit. It’s one of the famous causes of exclamation mark like hairs. Certainly extensive broken hairs can be a feature but other findings like black dots, V hairs, coiled hairs, hook hairs, hair powder just don’t appear to be a feature of this patient’s hair loss. I don’t think we’re dealing with trichotillomania.
Thallium poisoning
Of course, thallium poisoning is rare.
Dissecting Cellulitis and Alopecic and Aseptic Nodules of the Scalp
The description of the ‘painful bump’ is a bit unusual in the submitted question. It’s not typical of alopecia areata. It may be a ‘red herring’ and unrelated to the case here or it may truly be a valuable clue. Also, it would be helpful to know more about what is meant by a painful bump and how big of a bump is the individual referring to.
As we think about painful bumps, we need to think about small bumps and things like a folliculitis. As we get into larger and larger bumps we need to consider more significant inflammatory conditions of the scalp. Dissecting cellulitis can cause a larger dome shaped bump when it occurs and is famous for mimicking alopecia. Another closely related entity is “alopecic and aspetic nodules of the scalp” (AANS). AANS can resemble alopecia areata. The condition was first called “pseudocyst” but the name AANS was proposed in 2009 by Abdennader and Reygagne when it became clear that not all of these lesions show a pseudocyst morphology under the microscope.
The back of the scalp is a common area for AANS. Often patients present with just a single painful bump. Some authors feel that AANS is closely related to dissecting cellulitis.
Exclamation mark hairs have not been described in AANS but have been described in dissecting cellulitis.
Dome shaped area of hair loss on the vertex scalp, consistent with a diagnosis of alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp. Image from Anna Isabel Lázaro-Simó et al. Alopecic and Aseptic Nodules of the Scalp with Trichoscopic and Ultrasonographic Findings. Indian J Dermatol. Sep-Oct 2017;62(5):515-518. Image used with creative commons license.
Trichoscopic image from alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp (AANS), also known as pseudocysts. There are black dots, yellow dots, vellus hairs and broken hairs. Image from Anna Isabel Lázaro-Simó et al. Alopecic and Aseptic Nodules of the Scalp with Trichoscopic and Ultrasonographic Findings. Indian J Dermatol. Sep-Oct 2017;62(5):515-518. Used with creative commons license.
Trichoscopy of alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp. Image from Khalil I. Al-Hamdi and Anwar Qais Saadoon. Alopecic and Aseptic Nodules of the Scalp with a Chronic Relapsing Course. Int J Trichology. 2019 Nov-Dec; 11(6): 244–246. Used with creative commons license.
There are three stages of appearance to AANS lesions as described by Al-Hamdi and colleagues. It’s important to understand this - especially in this case.
Stage 1: Firm nodule. A firm and often tender nodule is present and the nodule lasts 1-3 weeks. There may be lymphadenopathy. If the nodule is punctured, it does not usually express any fluid. But if it does, the fluid is sterile and does not grow bacteria
Stage 2: Fluctuant Nodule with Hair Loss. In this stage, the nodule becomes less tender and hair loss is clearly seen. If the lesion is punctured in this stage a yellow fluid is expressed. This stage lasts 3-7 days.
Stage 3: Patchy Hair Loss Stage. In this stage, the nodule is no longer present as it has flattened either spontaneously or by puncture. This stage may last 2-3 month at which point hair growth normally occurs. It’s common in this stage for the patchy hair loss to be given a diagnosis of alopecia areata.
Was the bump described by the patient in this case actually stage 1 or stage 2 of AANS? Clearly, more information is needed. I would say it’s still quite unlikely.
Infections (Syphilitic Alopecia)
In a case like the one presented, one must never lose sight of alopecia areata as the most likely diagnosis. Most things fit well and it could be simply that this patch is more refractory and needs further steroid injections. However, we do need to consider rare mimickers (like AANS) - and another rare mimicker of syphilitic alopecia.
I don’t think that there is much in this case that makes a diagnosis of syphilitic alopecia high on the list. However, it can be a cause of patchy hair loss - especially with tapered exclamation mark like hairs, scale and redness like we see in the photos sent in by the patient.
Atypical trichoscopy of a patient with syphilitic alopecia in a 32 year old male. Exclamation mark like hairs are seen. Tapered bended hairs, erythematous background, diffuse scaling and perifollicular hyperkeratosis were present. Testing revealed a positive Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) at a titer of 1:256 and a reactive Treponema pallidum particle hemoagglutination assay. Image from Linda Tognetti et al. Syphilitic alopecia: uncommon trichoscopic findings. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017 Jul; 7(3): 55–59.
Other Diagnoses to Consider
There are several other diagnoses to consider here but they do not really have good evidence. These include:
tinea capitis
pressure alopecia
infiltrative conditions.
Tinea capitis
Tinea capitis can be a mimicker and the appearance can be altered by steroid injections. I don’t know the patient’s history well enough to know if there are predisposing factors that might make tinea capitis more likely. (In fact, I don’t have enough information in this patient’s history including information about the kidney surgery at 5 months post partum). It’s always possible that an inflammatory tinea developed and was flattened by steroid injections and persists in some manner. Of course, that’s unlikely and there do not really appear to be any trichoscopic features of tinea. There are no corkscrew hairs, comma hairs, bent hairs, i hairs, morse code hairs and no zig zag hairs. I don’t think this is tinea.
Pressure alopecia
In anyone with patchy hair loss after surgery, we need to consider pressure alopecia. It’s thought that hypoxia and altered blood flow predisposes to hair loss. Studies of patients with pressure alopecia have not suggested that exclamation mark hairs are part of the pressure alopecia diagnosis. Therefore, a diagnosis of pressure alopecia would not be likely in this case. According to Neema et al, trichoscopic findings of pressure alopecia include comedone- like black dots, black dots and area of scarring. In 2016, Francine Papaiordanou et al proposed that black dots, broken and dystrophic hairs were main features of pressure alopecia. In 2020, Tortelly et al proposed that black dots and vellus hairs were key features.
It’s not impossible that pressure from surgery facilitated the development of alopecia areata. in fact, R L Zuehlke et al in 1981 suggested that pressure may be a risk for alopecia areata too. So it’s going to be important to review if this area on the scalp shown in the photos had pressure during surgery. I don’t think it’s likely that what we’re seeing is related to pressure alopecia.
Trichoscopy of pressure alopecia showing black dots, broken and dystrophic hairs. In Image from Papaiordanou F et al. Trichoscopy of Noncicatricial Pressure-induced Alopecia Resembling Alopecia Areata. Int J Trichology. Apr-Jun 2016;8(2):89-90. Used with creative commons license.
Infiltrative conditions.
The term “infiltrative conditions” refers to a massively long list of cells that can enter into an area of the scalp (infiltrate) and cause localized hair loss. A variety of inflammatory and neoplastic cells can trigger patchy hair loss so one needs to always keep these in mind. They don’t usually cause exclamation mark hairs. Alopecia neoplastica refers to hair loss from metastatic cancer and can mimic alopecia areata in some cases.
This would not be expected in this case but this is added to the list and discussed here for completeness as we review patchy hair loss and considerations in the setting of refractory patchy hair loss. It does seem that hair is growing back in your case which makes infiltrative type causes quite unlikely. I don’t have a good sense of the time course of the photos you’ve submitted so that too would need to be carefully reviewed.
Alopecia neoplastica due to breast cancer. Image from Efthymia Skafida et al. Secondary Alopecia Neoplastica Mimicking Alopecia Areata following Breast Cancer.Case Rep Oncol. 2020 Jun 11;13(2):627-632. Image used with creative commons license.
Alopecia neoplastica due to breast cancer. Image from Efthymia Skafida et al. Secondary Alopecia Neoplastica Mimicking Alopecia Areata following Breast Cancer.Case Rep Oncol. 2020 Jun 11;13(2):627-632. Image used with creative commons license.
Conclusion and Summary
Thank you for this question. There are a few important points here in this case as we conclude. The first is that a full history and full examination are needed. This area is the area that you have photographed but one needs to always examine the entire scalp. A full history is needed of health and medical conditions over the past 31 years. The reason for the kidney surgery is completely unknown and would need to be included in the full story. I need to know everything about patients to confirm diagnoses with absolute certainty.
That said, the photos and clinical case still fit with undertreated alopecia areata as a top diagnosis. The exclamation mark hairs here and vellus hairs and regrowing hairs support this diagnosis. There are mimickers of course and these need to be considered.
For my own patients with similar stories I would first take a full history and do a full examination of the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes and body hair. Then I might inject with 2.5 mg per mL triamcinolone acetonide (steroid) with 2 to 3 mL injected into the area. I would not be too concerned if hair does not immediately grow back as it might take 2-3 sessions one month apart. I would not do more frequent than this. There is an option to add topical minoxidil to the plan but you’d want to review side effects with your supervising doctor.
If the area was slow to regrow I might add periodic use of clobetasol and minoxidil at home while doing these steroid injections.
Your photos would suggest you are already growing back significant hair.
If the area did not respond, I might do a biopsy. I don’t see this as necessary right now. The area needs to be properly treated and then if it does not respond to proper treatment, one can move on to step 2.
I don’t see AANS as a likely diagnosis (alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp), or pressure alopecia as being likely. We don’t see exclamation mark hairs in most cases of pressure alopecia. It would be helpful to know just how lumpy or raised this area was when you noticed it as this might lead one to at least consider AANS. The reality is that even if it is AANS and it’s some unusual pattern of exclamation mark hairs, it should respond to steroid injections at this point. I don’t think it’s likely we’re dealing with AANS.
Finally, anyone with this story should have blood tests for CBC, TSH, ferritin, vitamin D, creatinine. An antidandruff shampoo should continue to be used. Ketoconazole is reasonable. As mentioned, a biopsy will be needed if the area is not responding to appropriate doses of steroid injections (+/- minoxidil or clobetasol).
A full scalp examination is needed to determine if there are any other issues too. The area to the front may be thinner than prior years and that needs to be evaluated. It could be part of a resolving telogen effluvium or another diagnosis. A full examination of the scalp is needed in this case (as well as full examination of eyebrows, eyelashes and body hair as mentioned)
Thanks again
REFERENCE
Anna Isabel Lázaro-Simó et al. Alopecic and Aseptic Nodules of the Scalp with Trichoscopic and Ultrasonographic Findings. Indian J Dermatol. Sep-Oct 2017;62(5):515-518.
Khalil I. Al-Hamdi and Anwar Qais Saadoon. Alopecic and Aseptic Nodules of the Scalp with a Chronic Relapsing Course. Int J Trichology. 2019 Nov-Dec; 11(6): 244–246.
Abdennader S, Reygagne P. Alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp. Dermatology. 2009;218:86.
Linda Tognetti et al. Syphilitic alopecia: uncommon trichoscopic findings. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017 Jul; 7(3): 55–59.
Neema S et al. Trichoscopy of Pressure-Induced Alopecia and Alopecia Areata: A Comparative Study. Int J Trichology. Jan-Feb 2022;14(1):17-20.
Papaiordanou F et al. Trichoscopy of Noncicatricial Pressure-induced Alopecia Resembling Alopecia Areata. Int J Trichology. Apr-Jun 2016;8(2):89-90.
Tortelly et al,Pressure-Induced Alopecia: Presence of Thin Hairs as a Trichoscopic Clue for the Diagnosis Skin Appendage Disord. 2020 Jan; 6(1): 48–51.
R L Zuehlke et al. Pressure-potential alopecia areata. Am J Orthod . 1981 Apr;79(4):437-8.
Efthymia Skafida et al. Secondary Alopecia Neoplastica Mimicking Alopecia Areata following Breast Cancer.Case Rep Oncol. 2020 Jun 11;13(2):627-632.